It is a broad term for many disorders that impair the functioning of the muscles, either directly involving the muscles, or indirectly by involving nerves and the junction of nerves with the muscles. They may present as weakness, loss of muscle bulk, cramps, numbness and host of other symptoms including droopy eyelids, double vision and difficulty in swallowing. There are varied causes for this group of disorders including genetic defects, infections, autoimmune and related to certain drugs. They are diagnosed using a range of tests including electrical tests like Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies for muscle and nerve respectively. Treatment varies widely according to individual disorder. Some conditions are more easily treated than others.
What is EMG & NCV?
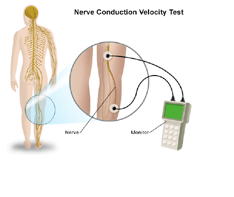
Nerve Conduction Velocity (NCV) :
A nerve conduction velocity (NCV) test measures how fast an electrical impulse moves through the nerve. NCV can identify nerve damage. During the test, nerve is stimulated with electrode patches attached to your skin. Two electrodes are placed on the skin over your nerve. One electrode stimulates your nerve with a very mild
1. Electromyography (EMG) :
Electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic procedure to assess muscles and the nerve cells (motor neurons). EMG results can reveal nerve dysfunction, muscle dysfunction or problems with nerve-to-muscle signal transmission.
EMG results are necessary to help diagnose conditions such as:
- Muscle disorders, such as muscular dystrophy or polymyositis
- Myasthenia Gravis
- Disorders of peripheral nerves – peripheral neuropathies
EMG is a low-risk procedure, and complications are rare.
